Modeling for Low Power Bypass Window SAR ADC Based on Highest Weight Capacitor Splitting
Abstract
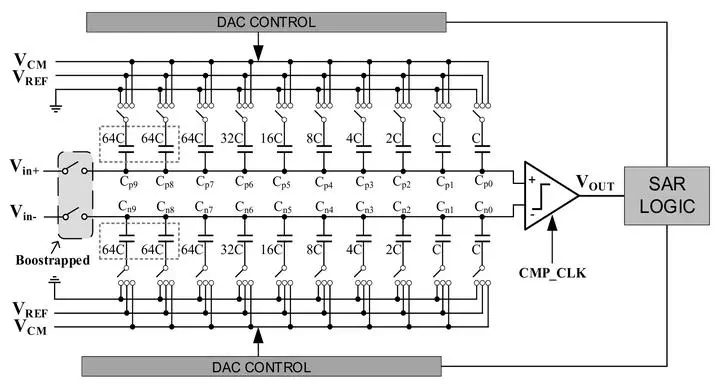
A 10-bit low power successive approximation register (SAR) analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with bypass window timing based on highest weight capacitor splitting is proposed. Different splitting schemes are analyzed and compared. By establishing a behavioral model in MATLAB, the power consumption of quantizing uniformly distributed signals for each splitting scheme is simulated. The results show that the lowest power consumption is 79.08 CVREF^2, which saves 94.7% and 53.5% compared with the conventional switching timing and VCM-based timing respectively. The proposed bypass window quantization scheme has more obvious advantages of low power consumption to quantize physiological signals like electrocardiogram (ECG). It can also improve the accuracy and linearity of the ADC. The paper also analyzes the influence of capacitor mismatch, comparator offset and input noise on the performance of the ADC, and evaluates their impact under different splitting schemes through MATLAB. The simulation results show that with 1% capacitor mismatch error, the “64+64” scheme can achieve an effective number of bits (ENOB) of 9.9 bit.