A High-Impedance 3-MOSFET Pseudo-Resistor for Instrumentation Amplifiers of Biomedical Sensors
Abstract
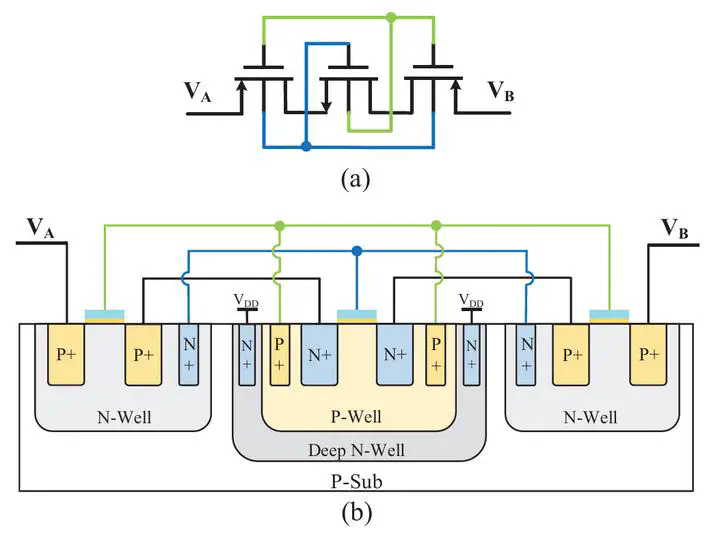
The pseudo-resistor (PR) is widely used in biomedical sensor applications. It has a large resistance within an acceptable die area. This paper proposes an improved MOS PR structure with large resistance value, wide operating voltage range, and high linearity. By introducing an nMOS transistor in the traditional back-to-back 2-pMOS structure, the resistance value of the PR in this design is effectively increased, especially under the condition of low voltage difference. The proposed 3-MOS structure was selected after a comparison of different PR connection topologies. Its performance in terms of linearity of response, symmetrical dynamic range, frequency behavior and simplicity of implementation is considered. Simulation results based on a standard 0.18 μm CMOS process show that the proposed 3-MOS PR provides a resistance of about 430 GΩ in the voltage range of ± 1 V. In the case of low voltage difference, the 3-MOS PR is improved by about 170 GΩ compared with the traditional PR. Finally, an AC-coupled instrumentation amplifier for bio-electrical signal acquisition is designed and simulated using the proposed 3-MOS PR, and a low-frequency corner of 0.48 Hz is achieved. The output time-domain electrocardiogram (ECG) signal verifies the feasibility of the 3-MOS PR.